Measure drag coefficient
aerodynamics plays a very important role in measuring the performance of blimp.
We know drag equation:
\[ F_D = \frac{1}{2}C_d\rho A v^2\]
where,
\(F_D\) is the drag force,
\(\rho\) is the density of the fluid,
\(A\) is the cross sectional area
\(v\) is the speed of the object relative to the fluid
\(C_d\) is the drag coefficient,
\(C_d\)
\(C_d\) is the drag coefficient. It's a dimensionless number. For different object with different shape, due to the different conditions when discharging fluid, their coefficient would be different.
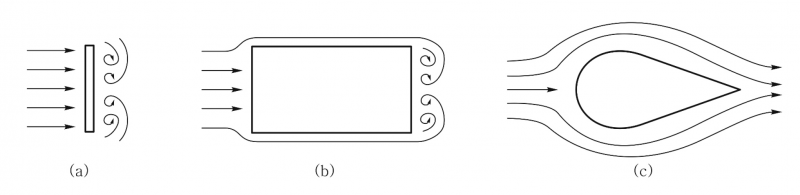
Take the following objects as example.
When they face the fluid, their front side will be depressed by the fluid, and due to the back side of flat board and cylinder is flat, fluid will have some local vacuum, which will generate vortex. The vortex will lengthen as the air velocity increases, causing "von Kármán vortex street", which will creates a drag force behind it.
How to measure \(C_d\)
Here we only discuss the low-cost measurement methods:
-
Experimental method -- Orifice plate
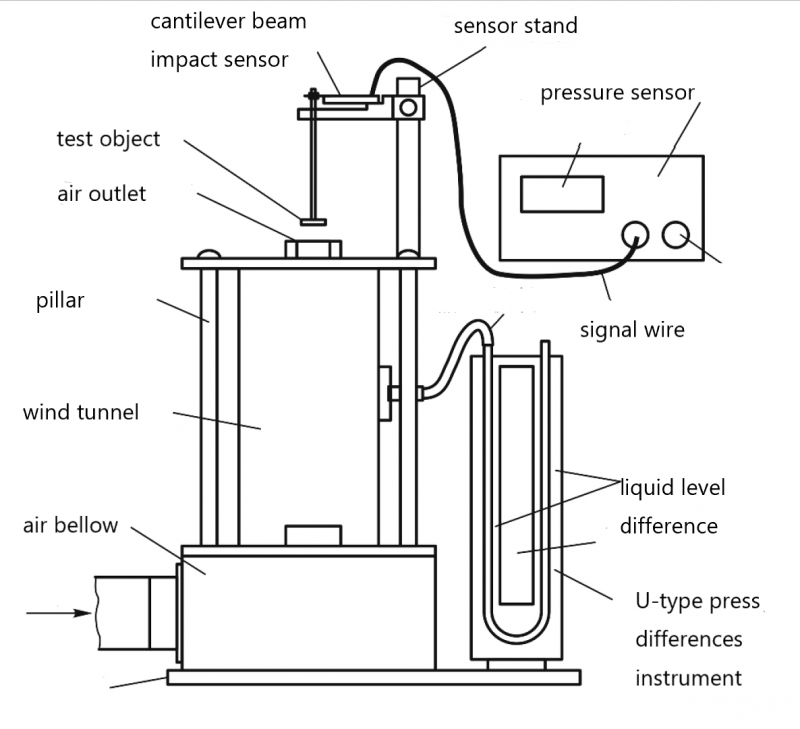
-
Experimental method -- object falling method

-
Software method -- Ansys fluent
